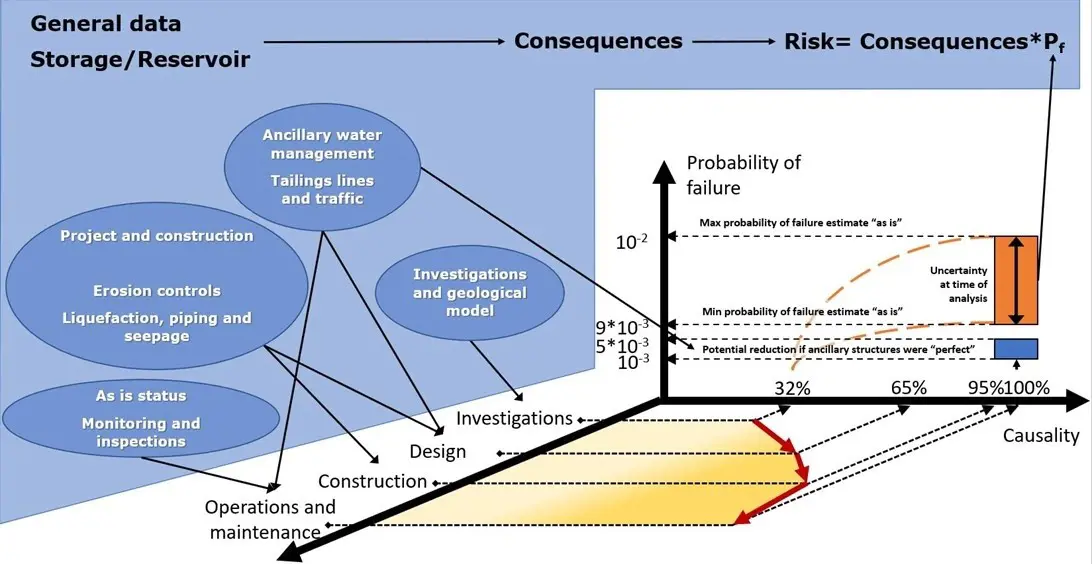
As one can see in the figure above, the probability of failure resulting from the composition of the KPIs evolves throughout the dam life while it maintains a certain level of uncertainties.
Key Risk Indicators/Key Performance Indicators used in ORE2_Tailings
In this section we show the ORE2_Tailings KPIs/KRIs and the corresponding DNxx. DNxx are the basic data required to run ORE2_Tailings and allow users to develop the causality analysis, evaluate any normalization of deviance and include uncertainties in the analyses.
The normalization of deviance and the uncertainties enter in the ORE2_Tailings probability of failure estimates as well as in the causality analysis.
General
This family includes general data on the system including year of construction, such as dam country, coordinates, length, max height, section type and materials and activity level (active, inactive or closed).
Storage
This section describes the storage and its contents, such as type and volume of main stored material, supernatant pond surface area, tailings surface area, average beach length, minimum beach length, and beach slopes.
Ancillary Water Management
Ancillary water management is one of the two main elements of the considered system. It is evaluated separately from the dam body itself as it may drive overtopping and other failure modes chains, like riverine erosion at the toe, collapse of bridges and other infrastructures capable of obstructing spillways and malfunctioning of decants.
Information we take into account for the ancillary water management facilities are:
- water balance event descriptions, including near misses and return
- weir and spillway age, design parameters and criteria, any accidents or near misses, status, maintenance, repairs, obstructions and bridges
- decant gallery age, design parameters and criteria, any accidents or near misses, status, maintenance and repairs
- diversion ditches age, design parameters and criteria, any accidents or near misses, status, maintenance, repairs and obstructions
Investigations and Geological Model
Future failure of the dam may be seeded in poor investigations and insufficient understanding of the geological model. Indeed, these can be seen as inceptual defects of the system.
Questions we ask are:
- What is the borehole density and depth with respect to structure height? What are the results of any tests and what assumptions informed those results?
- Is the geological/geotechnical model satisfactory and well understood?
- Are the geotechnical parameters and hydrological conditions used realistic?
- What are the seismic conditions? What acceleration and return were used in engineering analyses?
Project and Construction
Future failure may also be the result of past oversight, lack of care or incomplete analyses. ORE2_Tailings integrates the engineering analyses in the evaluation of the probability of failure, taking into account all the analyses performed and the results of those analyses, as well as any documentation of the construction process.
Liquefaction, Piping and Leaching
In our analysis, due attention is given to liquefaction and residual strength considerations. The final result integrates the presence and triggers of liquefiable materials, as well as whether the liquefiable materials are considered at peak or residual.
Tailings Lines and Traffic
This is indeed an often-neglected KRI, which can lead to unexpected exposures. These failure modes, so often considered minor, can be the initial trigger of cascading events which may develop into serious failures. They cannot be ignored or disregarded. They include equipment and traffic at top, in addition to details regarding their position and protection.
Erosion Controls
The KRIs cover all the elements in place to prevent or control erosion as well as possible malfunctioning symptoms indicative of lack of care or deviance. As a result, the compilation of the DNxx across the full spectrum leads to quantifying the normalization of deviance.
Erosion controls considered are berms, surficial drainage, internal drainage parameters and piping specifications.
“As is” Status
This is another family of KRIs contributing to the “good quality” of the system that are informative about any possible normalization of deviance. We look at any alterations or divergence from plans, known errors or omissions, unrepaired damages, and any history of issues, or near misses.
Monitoring and Inspections
For this KRI, we look at types and positioning of monitoring devices, any reported deformations or movements, inspections and past reports, and any independent reviews.
Closing Remarks on Data Required to Run ORE2_Tailings
The data required to run ORE2_Tailings are the DNxx, which can be derived from archival information and a site visit if possible and necessary. The evaluation of the DNxx allow us to include uncertainties in the evaluation of the probability of failure of the dam system.
The evaluation of the DNxx requires an attentive study of the knowledge base, i.e. archival documentation, past inspections, monitoring reports, and any available historical aerial imagery.
ORE2_Tailings analyses can be easily updated as new information becomes available by altering the values of the DNxx.